-
Delegate의 기본, 배열에서 홀수와 짝수 찾기 + Delegate 예제C# 예제 공부일기 2020. 7. 22. 19:23
정수에서 홀수와 짝수의 개수를 출력하는 프로그램이 있다.
int[] arr = new int[] {3,5,4,2,6,4,6,8,54,23,4,6,4} Console.WriteLine("짝수의 개수 : " + EvenCount(arr)); Console.WirteLine("홀수의 개수 : " + OddCount(arr));짝수의 개수를 리턴하는 EvenCount() 홀수의 개수를 리턴하는 OddCount static int EvenCount(int[] a)
{
int cnt =0;
foreach(var n in a)
{
if(n%2==0)
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}static int EvenCount(int[] a)
{
int cnt =0;
foreach(var n in a)
{
if(n%2==1)
cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}위의 두 소스코드를 보면 조건문 안에 n%2==0 과 n%2==1 만빼고 모두 동일한 코드이다. 이 두개를 하나로 만들고 싶을 때 쓰는 게 델리게이트이다. 델리게이트는 대리자라는 뜻으로 메소드의 참조, 즉 C언어의 함수 포인터와 같은 개념이다. 델리게이트는 다음과 같이 선언한다. delegate 키워드를 제외하면 일반 메소드의 선언과 동일하다.
delegate 리턴형식 이름(매개변수 목록);델리게이트를 사용하여 Count 메소드를 하나로 만든다. 정수를 매개변수로 하고 부울값을 리턴하는 델리게이트 MemberTest를 선언한다. Count 메소드에서 홀수일 때 true를 리턴하는 IsOdd() 와 짝수일 때 true를 리턴하는 IsEven()을 매개변수 델리게이트 testMethod로 전달받아 사용한다.
class Program { delegate bool MemberTest(int a); static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = new int[] { 3, 5, 4, 2, 6, 4, 6, 8, 54, 23, 4, 6, 4 }; Console.WriteLine("짝수의 개수 : " + Count(arr,IsEven)); Console.WriteLine("홀수의 개수 : " + Count(arr,IsOdd)); } static int Count(int[] a, MemberTest testMethod)//MeberTest형의 testMethod { //즉 변수처럼 메소드를 저장시켰다. //IsEven과 IsOdd가 testMethod자리에 들어간다. int cnt = 0; foreach (var n in a) { if (testMethod(n) == true) //밑의 Is메소드에서는 반환이 bool이다. cnt++; } return cnt; } static public bool IsOdd(int n) { return n % 2 != 0; }//나머지가 0이 아니라면 True반환 static public bool IsEven(int n) { return n % 2 != 1; }//나머지가 1이 아니라면 True반환 }위 예제에서는 n%2==0 과 n%2==1 요 부분을 각각
홀수라면 true을 반환하고 짝수라면 false을 반환하는
static public bool IsOdd(int n) { return n % 2 != 0; }
메소드 생성
짝수라면 ture를 반환하고 홀수라면 false를 반환하는
static public bool IsEven(int n) { return n % 2 != 1; }
메소드 생성
Count메소드의 매개변수를 보면 개수를 구할 배열 int[] a, 그리고 짝수개수를 구할지 홀수개수를 구할지 선택하는 메소드인 MemberTest testMethod가 있다. 제일 처음에 델리게이트로 선언한 MemberTest이기 때문에 testMethod자리에 IsEven과 IsOdd가 올 수 있게 된다. 마치 메소드 변수같은 느낌이다.
delegate bool MemberTest(int a)
bool IsOdd(int n)
bool IsEven(int n)
델리게이트로 만든 MemberTest와 나머지 2개의 매개변수와 반환타입이 똑같은 것을 볼 수 있다.
예제 몇개 추가
delegate int Calculation(int a,int b); static int Add(int a, int b){ return a+b;} static int Div(int a, int b) { return a / b; } static int Sub(int a, int b) { return a-b; } static int Mul(int a, int b) { return a*b; } static void Main(string[] args) { int iResult; Calculation[] aCalculator = new Calculation[] {Add,Sub,Mul,Div }; foreach (var item in aCalculator) { iResult = item(3,4); Console.WriteLine(iResult); } //for(int i=0;i<aCalculator.Length;i++) //{ // iResult = aCalculator[i](3, 4); // Console.WriteLine(iResult); //} }
class Program { delegate int NewType(int a); static int OnePlus(int a) { return a + 1; } static int TenPlus(int a) { return a + 10; } public static void Main(string[] args) { int TestNum = OnePlus(100); Console.WriteLine(TestNum); NewType aNuewType = new NewType(OnePlus); TestNum = aNuewType(100); Console.WriteLine(TestNum); NewType bNuewType = new NewType(TenPlus); TestNum = bNuewType(1000); Console.WriteLine(TestNum); } }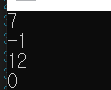
namespace tessss { class Mathematics { delegate int CalcDelegate(int x, int y); static int Add(int x, int y) { return x + y; } static int Subtract(int x, int y) { return x - y; } static int Multiply(int x, int y) { return x * y; } static int Divide(int x, int y) { return x / y; } CalcDelegate[] methods; public Mathematics() { methods = new CalcDelegate[] { Mathematics.Add, Mathematics.Subtract, Mathematics.Multiply, Mathematics.Divide }; } public void Calculate(char opCode, int operand1, int operand2) { switch (opCode) { case '+': Console.WriteLine("+ : " + methods[0](operand1, operand2)); break; case '-': Console.WriteLine("- : " + methods[1](operand1, operand2)); break; case '*': Console.WriteLine("* : " + methods[2](operand1, operand2)); break; case '/': Console.WriteLine("/ : " + methods[3](operand1, operand2)); break; } } } class Program { delegate void WorkDelegate(char arg1, int arg2, int arg3); static void Main(string[] args) { Mathematics math = new Mathematics(); WorkDelegate work = math.Calculate; work('+', 10, 5); work('-', 10, 5); work('*', 10, 5); work('/', 10, 5); } } }delegate int CalcDelegate(int x, int y); class MessageMap { public char opcode; public CalcDelegate Calc; public MessageMap(char opcode,CalcDelegate Calc) { this.opcode = opcode; this.Calc = Calc; } } class Mathematics { CalcDelegate[] methods; MessageMap[] amessageMaps; static int Add(int x, int y) { return x + y; } static int Subtract(int x, int y) { return x - y; } static int Multiply(int x, int y) { return x * y; } static int Divide(int x, int y) { return x / y; } static int per(int x, int y) { return x % y; } public Mathematics() { amessageMaps = new MessageMap[]{ new MessageMap('+',Mathematics.Add), new MessageMap('-',Mathematics.Subtract), new MessageMap('*',Mathematics.Multiply), new MessageMap('/',Mathematics.Divide), new MessageMap('%',Mathematics.per) }; } public void Calculate(char opCode, int operand1, int operand2) { Console.Write(opCode + ":"); foreach (var item in amessageMaps) { if(item.opcode==opCode) Console.WriteLine(item.Calc(operand1, operand2)); } } } class Program { delegate void WorkDelegate(char arg1, int arg2, int arg3); static void Main(string[] args) { Mathematics math = new Mathematics(); WorkDelegate work = math.Calculate; work('+', 10, 5); work('-', 10, 5); work('*', 10, 5); work('/', 10, 5); work('%', 10, 6); } }'C# 예제 공부일기' 카테고리의 다른 글
Func와 Action으로 델리게이트를 더 간단히 만들기 (0) 2020.07.22 이름 없는 델리게이트(Anonymous Delegate) (0) 2020.07.22 인덱서 (0) 2020.07.22 SortedList와 Sorted<TKey, TValue> (0) 2020.07.21 Hashtable과 Dictionary<TKey, TValue> (0) 2020.07.21